Vitiligo: NLRP1
RNAi
RNA interference (RNAi) is a valuable tool used by scientists to discover the roles of genes in organisms. It is a system used within living cells to control the activity of genes. RNA interference can be produced by using small RNA molecules (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA). These RNAs bind to specific regions of mRNA and serve to increase or decrease their activity - by regulating the amount of protein produced.RNAi is frequently used in model organisms Drosophila and C. elegans.
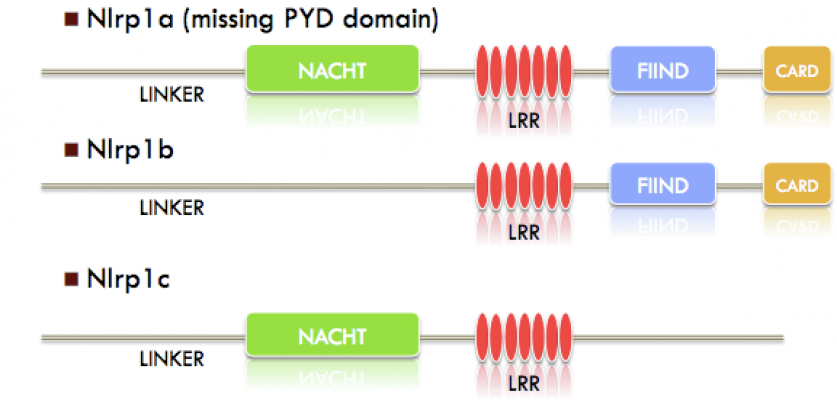
Homology searches for the NLRP1 gene yielded no homologs found in C. elegans or Drosophila. Thus, finding RNAi experiments in these organisms that related to the NLRP1 gene found in humans was difficult. However, the mouse is frequently used as a model organism for studying vitiligo. While RNAi models for vitiligo are not available based on the research I conducted, I have included information about the mouse models that have been used to study vitiligo in mice, in which a gene knockout is used. As stated in the homology section, mice have three paralogs that show homology to the NRLP1 gene. (See below)
Homology searches for the NLRP1 gene yielded no homologs found in C. elegans or Drosophila. Thus, finding RNAi experiments in these organisms that related to the NLRP1 gene found in humans was difficult. However, the mouse is frequently used as a model organism for studying vitiligo. While RNAi models for vitiligo are not available based on the research I conducted, I have included information about the mouse models that have been used to study vitiligo in mice, in which a gene knockout is used. As stated in the homology section, mice have three paralogs that show homology to the NRLP1 gene. (See below)
Mice have strong homologies as evidence by the tree generated by the computer software program STRING [1].
Mouse Model
Previous studies on vitiligo and other autoimmune diseases have relied heavily on mouse models that have been generated to exhibit vitiligo phenotypes. Below is an image taken from a study on vitiligo in 1986 [2] using the vit/vit mutant mouse model (white mouse). While the NLRP1 protein is not directly knocked out in this model, proteins related to immune response and cell death (e.g. caspase cascades, NALP3) have had their functions interrupted.
| a_mouse_model_for_vitiligo.pdf |
References
[1] STRING: http://string-db.org/
[2] Lerner, Aaron B., Tetsuo Shiohara, and Raymond E. Boissy. "A Mouse Model for Vitiligo."Journal of Investigative Dermatology 87 (1986): 299-304. EBSCO Host . Web. (See attached file)
This Web site was created as a project for Genetics 677 at UW-Madison, Spring 2010.
May 16, 2010. Sarah Hamilton.
May 16, 2010. Sarah Hamilton.