Vitiligo: NLRP1
Chemical Genetics

FASTA-formatted sequences of NLRP1 from both DNA and protein were entered into DrugBank [1]. Additionally a search query using "vitiligo" was used to generate a list of drugs used to treat vitiligo. The FASTA sequences generated alignments associated with the Niemann-Pick C1-like protein 1 - a protein used for the conversion of free micelles in the blood to esterified cholesterol in the gut and liver.
Vitiligo Drug Treatments
Monobenzone - Monobenzone is a drug used by patients with vitiligo to even out their skin tone. It is a depigmenting agent, causing loss of melanin in melanocytes.
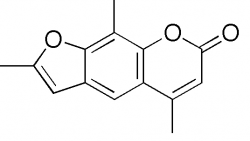
Trioxsalen
Trioxsalen - Trioxsalen (trimethylpsoralen, trioxysalen or trisoralen) is a furanocoumarin and a psoralen derivative. It is another drug that causes depigmentation in skin, thus evening out patches of variant pigmented skin in vitiligo patients. It causes photosensitization of the skin and is administered either topically or orally in conjunction with UV-A (the least damaging form of ultraviolet light) for phototherapy treatment of vitiligo. After photoactivation it creates interstrand cross-links in DNA, which can cause programmed cell death, much like mutant NLRP1 proteins do.
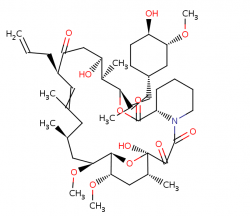
Tacrolimus
Tacrolimus - Tacrolimus has the opposite effect from the drugs listed above. It is an immunosuppressive drug whose main use is after organ transplant to reduce the activity of the patient's immune system. Since vitiligo is a caused by an overactive immune response, this drug counteracts the body's tendency to respond to stimuli causing such responses. It is used in a topical preparation and reduces peptidyl-prolyl isomerase activity by binding to the immunophilin FKBP-12 (FK506 binding protein) creating a new complex. This FKBP12-FK506 complex interacts with and inhibits calcineurin thus inhibiting both T-lymphocyte signal transduction and IL-2 transcription (observed in high levels in vitiligo patients) [1].
Analysis
While it seems unusual at first that a NLRP1 shares a strong homology with a protein whose function is specifically related to cholesterol transformation, further analysis suggests that these proteins may share a similar role. NLRP1 serves as an intermediate, much like NPCLP1, in that is responds to a stimuli (in NLRP1's case: MDP), causing a conformation change within its domain to yield a cascade event. NPCLP1 also serves as an intermediate between consumed free micelles and the esterified cholesterol particles in our liver.
References
[1] DrugBank: http://www.drugbank.ca
This Web site was created as a project for Genetics 677 at UW-Madison, Spring 2010.
Sarah Hamilton. May 17, 2010.
Sarah Hamilton. May 17, 2010.

