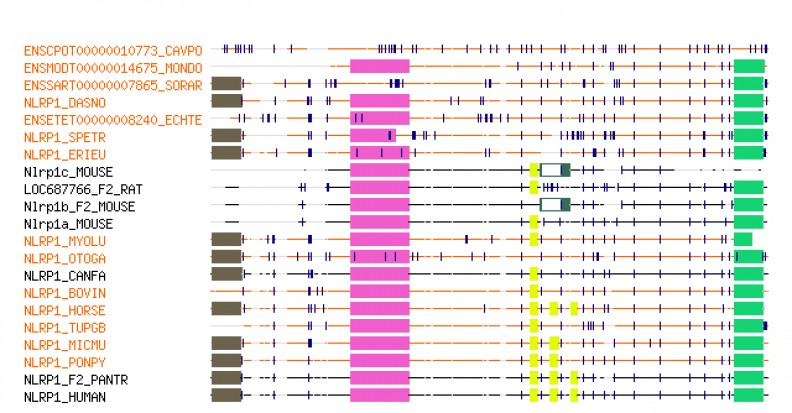
Vitiligo: NLRP1
Homologous Genes

Homologs of NLRP1 were obtained using the program Homologene[1]. Homologene produced five species with NLRP1 homologs. Using a BLAST search, gene and protein Expect (E) values for each species were determined based on sequence alignment.
Gene name: NLR family, pyrin domain containing 1 (NLRP1)
Gene accession number: NC_006484.2
E-value: 0.0
Protein accession number: XP_001167230.1
E-value: 0.0
Canis lupus familiaris (Dog)
Gene name: NLR family, pyrin domain containing 1 (NLRP1)
Gene accession number: NC_006587.2
E-value: 1e-47
Protein accession number: XP_001028225.1
E-value: 0.0
Bos taurus (Cow)
Gene name: NLR family, pyrin domain containing 1 (NLRP1)
Gene accession number: NW_001496266.1
E-value: 0.0
Protein accession number: XP_00125710
E-value: 0.0
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Gene name: NLR family, pyrin domain containing 1A (NLRP1A)
Gene accession number: NC_000077.5
E-value: 0.0
Protein accession number: NP_001004142.1
E-value: 0.0
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Gene name: NLR family, pyrin domain containing 1 (NLRP1)
Gene accession number: NC_005109.2
E-value: 0.0
Protein accession number: XP_340836.3
E-value: 0.0
FASTA txt files
1. Pan troglodytes
1. Pan troglodytes
| Pan troglodytes DNA FASTA |
2. Canis lupis familiaris
| Canis lupis familiaris DNA FASTA |
3. Bos taurus
| Bos taurus DNA FASTA |
4. Mus musculus
| Mus musculus DNA FASTA |
5. Rattus norvegicus
| rat_fasta_dna.rtf |
Protein FASTA for all species
| species_fasta_protein.txt |
Alignments
Clustal W, T-Coffee[3], and Muscle sequence alignments could not be generated from DNA FASTA sequences for the above species. Their sequence lengths exceed base pair limits of the online software programs. However, an alignment using protein sequences was generated from T-Coffee (see file attachment below). Additionally, an alignment was constructed by Tree Fam [4]using FASTA sequences obtained from sequenced animals.
| tcoffee-20100324-2018182590.clustalw.txt |
Analysis
Homology analyses of the NLRP1 gene was completed using DNA sequences from various species. Pan troglodytes, less formally known as chimpanzees, share the most common ancestry to humans, and thus their genomes are 98 percent similar to their human orthologs. Thus, BLAST searches of Homo sapiens and Pan troglodytes yield strong homology, as indicated by their statistically significant E-value of 0.0. Of notable importance is the fact that the remaining sequences used to complete this homology study are predicted sequences. Therefore, the NLRP1 gene sequence in the other listed species (excluding H. sapiens and P. troglodytes) remain to be sequenced.
References
[1]Homologene http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=homologene
[2]E-value http://people.sissa.it/~fenollar/Homology_modeling_tutorial.pdf
[3]T-Coffee http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/t-coffee/index.html
[4]Tree Fam http://www.treefam.org/
[2]E-value http://people.sissa.it/~fenollar/Homology_modeling_tutorial.pdf
[3]T-Coffee http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/t-coffee/index.html
[4]Tree Fam http://www.treefam.org/
This Web site was created as an assignment for Genetics 677 Spring 2010.
Sarah Hamilton, April 15, 2010
Sarah Hamilton, April 15, 2010